
Gallery of proteins
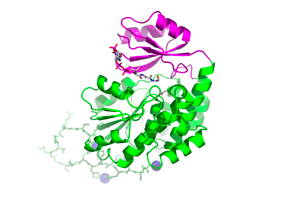
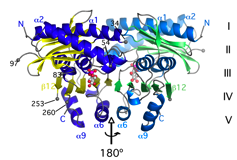
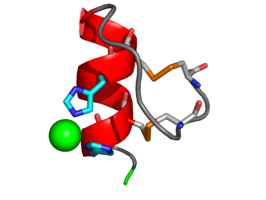
The structure of M. tuberculosis FabD was solved by MAD based on Ni2+ ions bound to the N-terminal His-tag (Ghadbane et al., 2007)
Inositol monophosphatase M. tuberculosis SuhB dimerizes upon binding of the activating ion Mg2+ (Brown et al., 2007)
B. subtilis levansucrase, here bound to substrate sucrose generates long-chain fructofuranosyl polymers (Meng & Fütterer, 2003)
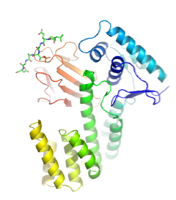
Transcriptional regulator EmbR, involved in regulating cell wall arabinan synthesis in mycobacteria (Alderwick et al., 2006)
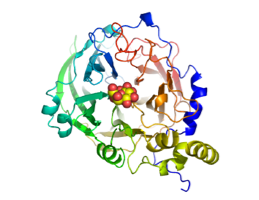
The secreted protein M. tuberculosis Ag85D is a catalytically inactive homolog of the subunits of the antigen 85 complex, and under consideration as a novel TB vaccine (Wilson et al., 2004)
The N-terminal IMD domain of the actin regulator IRSp53 forms a dimer that interacts with F-actin and the cell membrane (Millard et al., 2005).

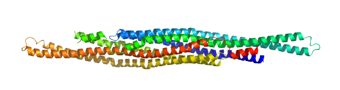
The TetR-like repressor M. tuberculosis EthR regulates transcription of the Baeyer-Villiger monooxygenase EthA, which is required for activation of the antitubercular drug ethionamide. (Dover et al., 2004)
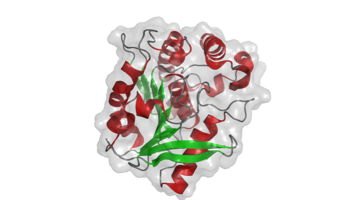
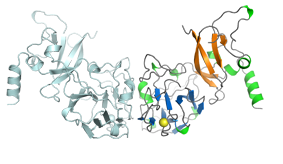
The structure of arabinosyltransferase M. tuberculosis EmbC (C-terminal domain) was solved by MAD. The isolated domain forms dimers in solution and displays a CBM-like domain that binds arabinosyl-acceptor analogs (Alderwick et al, 2011).
Mannosyltransferase PimB’ plays a key role in PIM biosynthesis, a mycobacterial cell wall component that influence the host immune system (Batt et al., 2010)